Azure Storage account key rotation is one of the most important things people forget about. Account keys provide full access to your storage; nevertheless, we fail to keep them safe and fresh.
In this article, we talk about the key rotation mechanisms provided by Microsoft Azure.
Why?
Azure Storage account provides two account keys that can manage the storage. They provide the user with the full power to read, modify, delete and create content. Not only that we need to keep them safe, but we also need to ensure that we rotate them at specific time intervals.
Key expiration policy
A key expiration policy can be easily created from the Azure Portal. When the policy is triggered, a reminder is displayed in the portal to remind us to rotate the keys. Additionally, once you have the key expiration policy defined, you can monitor the compliance of your storage account, including the key rotation.
As you can see above, this can be achieved from the Azure Portal or through the Azure CLI or PowerShell. The reminders can be daily, weekly, monthly or yearly OR custom.
Monitoring expired account keys
This can be achieved using Azure Policies. A built-in policy for Azure Storage covers the account key expiration. The policy can be applied to one storage account or to all storage accounts under a resource group or subscription.
Once you have defined the policy, you navigate to the Azure Policy dashboard to check the level of compliance.
We talked about defining a policy and monitoring the key expiration from the portal or from the Azure Policy dashboard.
What about automation? Can we configure the policy in such a way as to send a notification to an interval or external system?
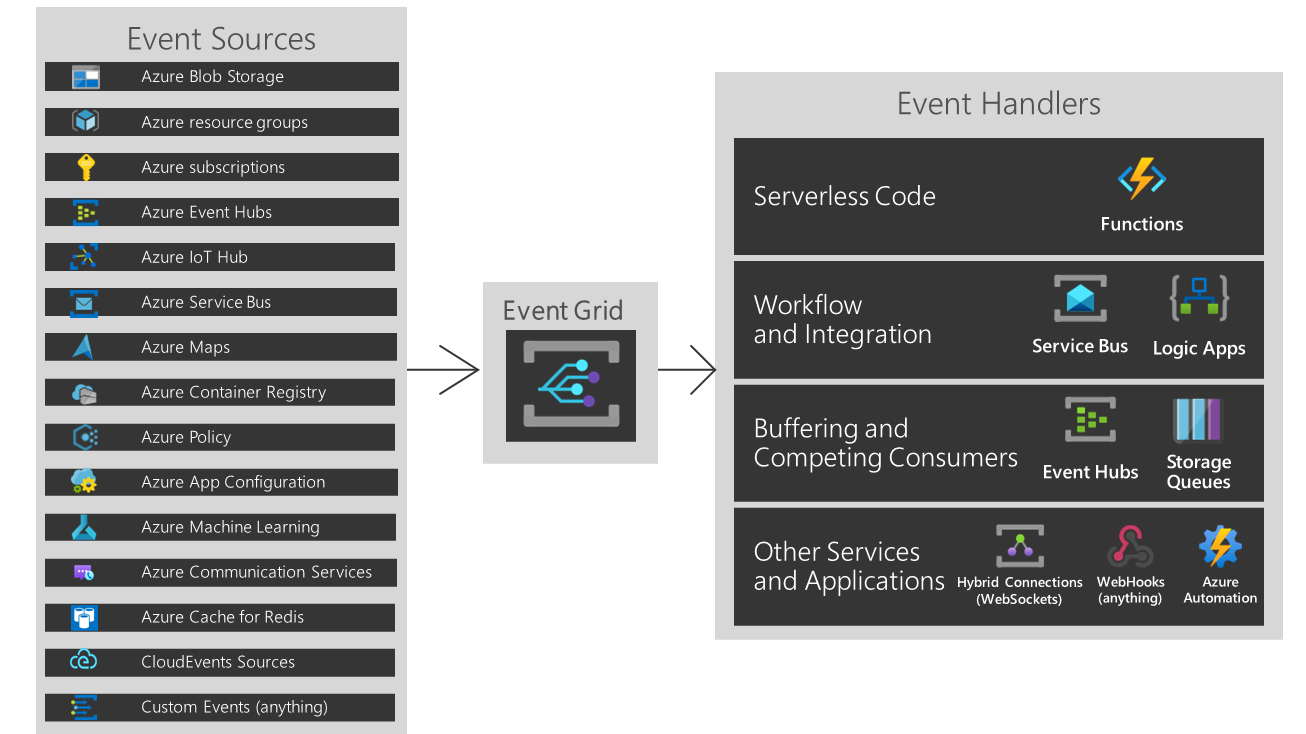
YES, we can do this. You would need to rely on Event Grid and ingest the events from Azure Policy. Once you have done this, you can decide what kind of action (event handled you would like) - Azure Functions, Logic App or Service Bus, Queues, WebHooks, Automation and so on.
You could even define an Azure Automation or an Azure Function that automatically rotate the key when the Azure Policy is triggered.
For more about how to react when an Azure Policy state changes, I recommend looking at this page.
Conclusion
Microsoft is offering us the capability to define alerts and policies, monitor them, and react to them. Azure Key Rotation capability is fully covered by Azure; we just need to ensure that we are configuring and integrating it in our systems.


Comments
Post a Comment